Student Will Continue to Read for Comprehension
Reading: IEP Goals & Strategies
Ways to improve Reading Comprehension:
- Use Visuals.
- Answer Questions.
- Predicting.
- Summarizing/Retelling.
- Identifying parts of story/text.
- Make a connection.
- Active readers.
See below for further explanation, as well as links to assessments and other valuable information.

If you are here, please make sure that you also read the blog posts about Inference and Working Memory, as they go hand in hand with Reading Comprehension.
How to Improve a Reader's Comprehension
Each child is different and will respond to different strategies. The devil is in the details: taking the time to get to know the child and what works for them.
Additionally, teachers or aides may deliver these strategies in a variety of ways. There is direct teaching, self-exploration, guided practice and so on. Just make sure that your child's IEP is a reflection of what they need. An unmotivated and frustrated student will likely need more direct instruction and not self-exploration (would likely goof off or daydream).
These are some of the common Reading Comprehension Strategies that schools use.

1. Create Visuals: Studies have shown that students who visualize while reading have better recall than those who do not (Pressley, 1977). This comes in many formats, including but not limited to-
- Graphic Organizers
- Venn Diagrams
- Elkonin Boxes
- Story Map/Storyboard
- Creating a visual in your mind
2. Answering Questions about what they just read: Asking and answering questions about a text is another strategy that helps students focus on the meaning of the text. Teachers can help by modeling both the process of asking good questions and strategies for finding the answers in the text. Questions can be effective because they:
- Give students a purpose for reading.
- Focus students' attention on what they are to learn.
- Help students to think actively as they read.
- Encourage students to monitor their comprehension.
- Help students to review content.
- Relate what they have learned to what they already know.
3. Predicting what will happen next: You can ask your reader to make a prediction about a story based on the title and any other clues that are available, such as illustrations. Later, ask him/her to find text that supports or contradicts their predictions.
4. Summarizing/Retell the Story: Summarizing requires students to determine what is important in what they are reading and to put it into their own words. Asking students to retell a story in their own words forces them to analyze the content to determine what is important. You can encourage your reader to go beyond recounting the story in literal language, to drawing their own conclusions about it.
5. Identify Main Idea, Characters, Story Line: This helps your reader understand the main parts of a text and its storyline. This can be done with words or visually.
6. Make a Connection/Past Experiences: When a reader previews text, he/she taps into what they already know that will help them to understand the text they are about to read. This provides a framework for any new information they read. Again, read the inference link above.
7. Active Reading: Consistent use of the above strategies combined with finding books and material that are of interest to the reader.
IEP Goals for Reading Comprehension
- When given a grade-level text, STUDENT will read and demonstrate comprehension of grade-appropriate literary texts (e.g., stories, legends, poems). (Use objectives to make this specific and measurable.)
- The Student will use total communication (AAC device, PECS, and verbalization) to read and demonstrate comprehension of at least 12 new functional vocabulary words and related short phrases through reading and then completing a variety of vocational activities given minimal gestural cues within the larger school environment (i.e. school building, campus) in 4/5 opportunities.
- The student will demonstrate reading comprehension of print texts with minimum assistance given 4/5 recorded opportunities.
- When presented with text on his instructional level, the student will use context clues to determine the meaning of unfamiliar words in reading materials with 80% accuracy, as measured by written work samples, by the end of (IEP Date).
- The Student will read and verbalize short phrases pertaining to vocational activities and complete functional vocational activities throughout the larger school environment (i.e. school building, campus) in 4/5 opportunities.
- After reading or looking at a simple storybook, STUDENT will identify the main idea 80% of the time 4 of 5 trials.
- When presented with a passage at the instructional level, STUDENT will read to confirm initial predictions with 80% accuracy 4 of 5 trials.
- After reading a story, STUDENT will explain the sequence of events with 80% accuracy four of five trials.
- Given minimum assistance, the student will read a short story (up to two paragraphs) and answer rotating who, what and where questions, why questions and how questions in 4/5 recorded opportunities.
- After reading a story at the instructional level, STUDENT will identify the main idea and two supporting details with 80% accuracy four of five trials.
- When presented with how, why, and what-if questions after reading a story silently, STUDENT will answer comprehension questions with 80% accuracy four of five trials.
- By (date), after reading a grade-level story, the student will ask a peer (5) questions that demonstrate understanding (e.g. "Why do you think Susan decided to leave the party?"), then answer (5) questions about the text asked by a peer in 4 of 5 trials as measured by teacher-charted records.
- When asked, STUDENT will identify homonyms, synonyms, and antonyms and use appropriately in sentences with 80% accuracy four of five trials.
- After reading a story, STUDENT will identify the effect of a certain action with 80% accuracy 4 of 5 trials.
- The Student will match pictures to words and words to pictures for a minimum of 20 new functional vocabulary words in 4/5 recorded opportunities, given visual support and minimum assistance.
- After reading a short passage and answering comprehension questions, STUDENT will locate, in the text, information to support answers, 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- The student will match sentences to pictures and pictures to sentences for a minimum of 20 new functional vocabulary words in 4/5 recorded opportunities, given visual support and minimum assistance.
- After reading a short passage, STUDENT will use implied meaning to answer comprehension questions, 4/5 times with 80% accuracy.
- Provided with visual support (i.e. color coding, highlighting, etc.), the student will read short text and answer "where" structure questions with minimal gestural assistance given 4/5 opportunities.
- After reading various statements, STUDENT will identify fiction and nonfiction statements, 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- Given minimum assistance, the student will demonstrate reading comprehension by completing two-step written directions, which encompasses reading two sentences and answering "who, what or where" questions in 4/5 recorded opportunities.
- After reading various statements, STUDENT will distinguish fact from opinion, 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- Provided with a short text (maximum of five sentences), the student will read and answer structure questions to demonstrate comprehension with minimal gestural assistance given 4/5 opportunities.
- After being given various information, STUDENT will use text organizers to locate and categorize information in printed material, 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- The student will answer inferential questions (i.e. "How does the main character feel after the event?") regarding print text with minimum assistance given 4/5 recorded opportunities.
- After reading a passage, STUDENT will recognize the figurative use of language, 4/5 times with 80% accuracy.
- IEP Student will increase comprehension of a variety of printed materials to ___________- as measured by
___________ (running records, IRI, anecdotal data, observation, performance assessment, etc.) - After reading a passage, STUDENT will identify the mood of the reading selection with 80% accuracy 4 of 5 trials.
- Provided with visual support (i.e. color coding, highlighting, etc.), the student will read a short text (maximum of five sentences) and answer "what" structure questions with minimal gestural assistance given 4/5 opportunities.
- After reading a story, STUDENT will identify details most important to the plot with 80%accuracy 4 of 5 trials.
- Given visual support, the student will demonstrate comprehension of at least 12 new functional words, including vocational and safety vocabulary, as demonstrated by the following objectives with minimal gestural cues within the larger school environment (i.e. school building, campus) in 4/5 opportunities.
- ________ will increase ability to understand and respond to literature from various genres and geo-cultural groups to __________ as measured by _______ (State Scoring Guide, teacher survey, performance assessment, etc.)
- When given a reading passage, STUDENT will use questioning strategies to increase comprehension of what was read 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- After reading a passage, STUDENT will understand the passage's tone, character, point-of-view, and theme 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- After reading a passage, STUDENT will identify the author's purpose 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- After reading a passage, STUDENT will recognize the difference between fact and opinion 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- When given a passage, STUDENT will read and predict the outcome 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- After reading a passage, STUDENT will recognize the figurative use of language 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- After reading a passage, STUDENT will identify the cause of the situation 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
- After reading a passage, STUDENT will predict the main problem 4/5 times with 90% accuracy.
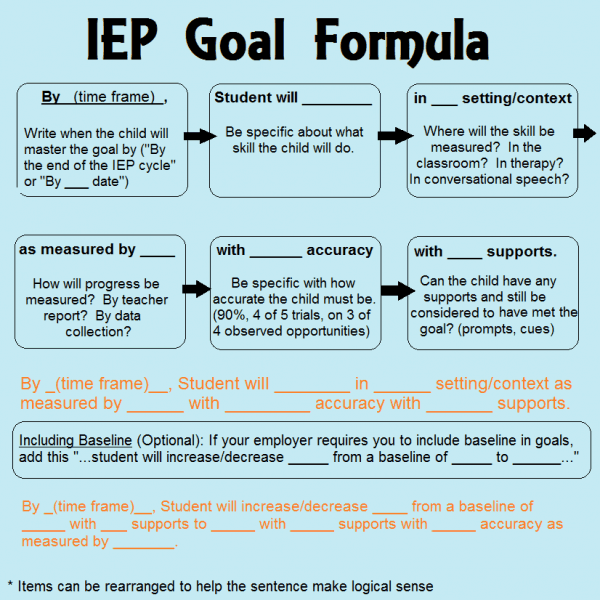
As always, you can put any of the above goals into the IEP goal formula to make sure that it is relevant and measurable.
Please note, I also have: IEP Goals for Writing Skill s
Examples of IEP Reading Goals
Here are other areas of reading, though most of this post focuses on comprehension.
- Decoding-By the end of the IEP period, when given a list of 40 multisyllabic words containing closed, open, consonant-vowel-e, and vowel team syllable types, the student will be able to decode 36/40 words correctly as measured by teacher records.
- Fluency-By the end of the school year, the student will read grade-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression at 90 words per minute with 90% accuracy, as measured by teacher records on three consecutive occasions.
- Finding Key Ideas and Details-By the end of the IEP period, when given a skill-appropriate passage, the student will identify the main idea and provide at least three details related to the main idea with 90% accuracy in three out of four trials.
- Inferences– I have a whole separate post on inference.
- Vocabulary-By the end of the IEP period, the student will use context clues and other strategies, such as consulting a dictionary, to help determine the meaning of unfamiliar words, with 80% accuracy in four out of five opportunities.
Reading Comprehension: Websites for Kids and Parents
If you want to work with your child at home, here are some ideas. It might be as simple as having an evening reading discussion where you read a book/chapter to them, and discuss it afterward. Don't overthink it, but all parents should be encouraging their kids to read. Read a book together, then watch the movie.
Reading Websites for Parents
Strategies and suggestions to use at home in all areas of reading development. These include phonemic awareness, phonics, decoding, fluency, comprehension and reading aloud.
- Sites for Parents
- Literacy Matters
- Reading Rockets
- We Read: Literacy and Education for Life
- Family Education
- Reading Success Lab
- Read To Me
- Lit2Go
- RHL School Reading Comprehension
- Education.com
Comprehension Websites for Readers
- Bookshare
- ReadWorks
- Read Theory
- Roy the Zebra
- Reading is Fundamental
- Literacy Center
- Fun English Games
- Empire – a Goodgame Studios Strategy Game
- JumpStart
- Mr. Nussbaum Education Website
- National Geographic
Tests that evaluate Reading Comprehension
Remember, for IEP evaluations, schools are required to evaluate a child in every area of suspected disability. If they do not suspect it, you need to bring it to their attention. Also, once you get your evaluation results back, look up the protocols online. Many times a test is given to a child that evaluates reading skills, but not necessarily comprehension. If you disagree with your school district's findings, read about what an IEE is and how to ask for one.
There are other parts such as fluency and decoding. You want to make sure your child has been evaluated for the proper concern. Also, some test publishers only develop assessments for certain age groups or grades. These are just some of the evaluations to determine comprehension.
I've listed a few assessments below. You can visit their websites to see the protocols and criteria.
- List of 33 Reading Comprehension Evaluations
- Degrees of Reading Power (DRP), ERDA, GORT 5, ITBS/Iowa test, TPRI.
{this post was originally published in 2013 but was edited to check links}
Source: https://adayinourshoes.com/reading-comprehension-strategies/
0 Response to "Student Will Continue to Read for Comprehension"
Post a Comment